Introduction to MAC Access Control
In our digital era, security is paramount. MAC Access Control steps in to safeguard sensitive data with rigid access regulations. This section dives into the concept of MAC and its distinction from other models.
What is Mandatory Access Control (MAC)?
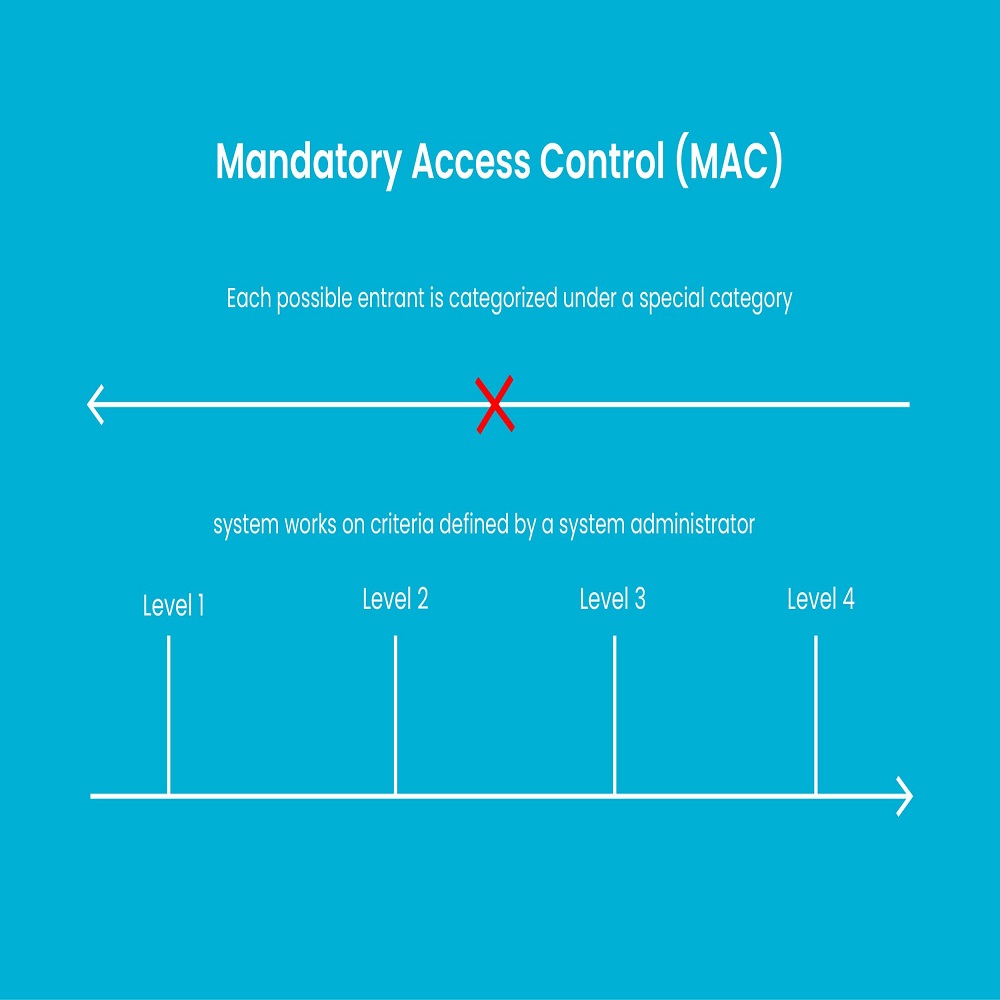
Mandatory Access Control, or MAC, is stringent. It’s all about access permissions based on user roles and data classification. At its core, MAC is about enforcing access based on predefined policies and, crucially, not leaving those decisions to users or data owners.
MAC restricts access to the need-to-know basis. It ensures that critical data stays within reach of only those with proper clearance levels. The MAC framework allows access strictly according to security policies, making it less about user discretion, more about mandatory regulations.
How MAC Differs from Other Access Control Models
Unique in its approach, MAC sets itself apart from other access control methods. Unlike Discretionary Access Control (DAC), MAC doesn’t permit users to set access permissions. Instead, it centralizes control within a trusted authority that dictates strict access hierarchy.
MAC, with its top-down control structure, ensures that data is accessible only to vetted and authorized individuals. In contrast, DAC allows owners of data to decide who gets access, introducing flexibility but also potential security lapses.
In summary, MAC is about strict regulation and non-discretion, while DAC and others might offer more flexibility but less stringent security. The choice between these models depends on an organization’s security needs and compliance requirements.
The Importance of MAC in Cybersecurity
In the realm of digital security, MAC access control plays a vital role. It keeps sensitive data safe from unauthorized eyes. Below, let’s explore how MAC fortifies cyber defenses and supports regulatory adherence.
Protecting Sensitive Data
MAC is essential for guarding key information. It does this by setting firm rules on who can see what data. For instance, only those with the right clearance can peek at classified files. This minimizes the chance of data leaks, keeping secrets well under wraps.
Businesses and organizations handle loads of personal and confidential data. Using MAC means they can trust that this delicate information won’t fall into the wrong hands. The control is meticulous, denying access to all but the most qualified individuals.
Compliance with Regulations and Standards
Many industries must adhere to strict guidelines. Think about healthcare or finance; they have rules like HIPAA or PCI DSS. MAC helps ensure that these standards are met with precision. It does this by controlling access to sensitive material, proving compliance.
Agencies and companies must often prove they’re handling data correctly. MAC aids in showcasing their commitment to stringent data security practices. It’s a clear way to say, ‘We take these regulations seriously and put the right protections in place.’
In summary, MAC is crucial in a world where data breaches can be costly. It protects crucial data and helps businesses keep in line with legal standards.
Implementation of MAC Access Control
Successfully implementing Mandatory Access Control (MAC) is crucial for any organization prioritizing data security. The following steps are key to an effective MAC setup.
Assessing Organizational Data Security Needs
The first step in implementing MAC is to comprehend the data security requirements of your organization. This involves:
- Identifying the types of sensitive data handled.
- Understanding legal compliance and industry standards.
- Assessing the potential risks and threats to your data.
- Gauging the level of access control needed based on data sensitivity.
This assessment will guide you in structuring your MAC system appropriately.
Defining User Roles and Security Labels
Once you know your data security needs, define clear user roles and security labels. These are essential to MAC implementation:
- Assign security labels to data that indicate its sensitivity level.
- Establish user roles within your organization.
- Grant user clearances that match security labels.
- Ensure that roles and labels accord with MAC policy and procedures.
With these measures in place, your MAC system can effectively restrict access to authorized individuals only, safeguarding critical information.
Advantages of MAC in Data Security
High-Level Data Protection
MAC offers top-tier security for sensitive data. It limits access based on strict rules. Only those with clearances can view certain information. This cuts the risk of data breaches. Companies can be sure their vital info stays safe with MAC.
Centralized Control and Management
With MAC, one authority controls data access. This simplifies oversight for organizations. It makes sure that all access follows set policies. Changes in access need approval from this central point. This leads to stronger data protection.
Immunity to Trojan Horse Attacks
MAC systems block unauthorized data sharing. They don’t let users lower data classifications. This stops Trojan Horse attacks from spreading. By preventing data declassification, MAC keeps your systems secure.
Common Use Cases for MAC
Mandatory Access Control (MAC) is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It fits best where data sensitivity is at its highest. Let’s consider where MAC is typically put to use.
Government and Military Data Security
Governments and military organizations handle classified data. For them, security can’t be a second thought. MAC offers a layer of protection that’s hard to breach. Here, every piece of data is tagged with a security level. Only those with matching clearances can access it. From operation plans to personnel files, MAC keeps these secrets safe.
Healthcare and Financial Information Protection
Next, healthcare and finance sectors deal with personal information daily. Patients’ health records and individuals’ financial data require tight security. MAC systems help by granting access only to approved individuals. A doctor can view a patient’s record, but the receptionist cannot. Likewise, only certain bank employees can see customer financial details. MAC ensures that these sensitive pieces of information stay protected and private.
Challenges of Using MAC Access Control
While MAC access control offers numerous security benefits, it comes with its own set of challenges. These challenges can prove critical for organizations when deciding on an access control model.
Complexity in Maintenance and Scalability
MAC systems require careful, ongoing maintenance. The rules and labels that govern access permissions need regular updates. This can lead to a large administrative burden, especially as an organization grows. Additionally, adding new roles or data classifications means updating the entire system accordingly. As a result, MAC lacks the scalability of less rigid access control models. Strict adherence to policies can be resource-intensive.
Potential Impact on Workflow
MAC can also impact workflow within an organization. Its rigid nature means that users often face hurdles when needing access for legitimate purposes. For example, an employee needing sudden access to certain sensitive data may experience delays. This can slow down the pace of work and reduce efficiency. Also, the need for high-level approval for access changes can add to the bureaucracy and impede swift decision-making.
In summary, MAC provides robust data security at the cost of maintenance complexity and potential workflow disruption. Understanding these challenges helps organizations balance security needs with operational efficiency.
Integrating MAC with Other Access Control Models
In the pursuit of secure systems, blending MAC with other models can enhance flexibility.
Combining MAC and DAC for Flexibility
Combining MAC and DAC models can grant both security and user freedom. DAC’s user-managed permissions offer adaptability. MAC provides the overarching security structure. Together, they protect essential data while allowing certain sharing among peers. For instance, within a corporate file system, MAC can guard sensitive records. DAC lets coworkers share non-critical data easily. Integrating both ensures a balance between security protocols and operational fluidity.
Using MAC for core security and DAC for less sensitive areas is smart. It maintains high protection where needed. It also supports day-to-day data exchanges that boost work efficiency. Effective integration requires clear guidelines on when and how each model applies.
Role-Based Access Control Enhancements
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) adds another layer to MAC systems. It streamlines user permissions by grouping them into roles. This reduces the burden of individual user management. MAC secures sensitive data. RBAC organizes access rights based on job functions. This helps speed up user access setups. It also maintains MAC’s strict security measures.
RBAC works well with MAC in large organizations. It manages user access without compromising on security policies. It groups user permissions, making it easier to assign and adjust access as needed. Businesses gain efficiency and keep control over who sees what within the company.
In conclusion, integrating MAC with DAC and RBAC can offer the best of both worlds. It combines strict data security with the operational advantages of role-based permissions. For organizations, it’s about finding the right mix to meet their specific security and workflow needs.
Conclusion
The journey through Mandatory Access Control (MAC) highlights its role in protecting data. It’s clear that MAC is fundamental in environments where security cannot be compromised. Recognizing when to apply MAC is key for any organization handling sensitive information.
Assessing the Need for MAC in Your Organization
Evaluating your organization’s need for MAC involves several steps:
- Review the data sensitivity you handle.
- Look at the compliance and regulations you must follow.
- Quantify the risks and threats to your data security.
- Determine if MAC aligns with your security strategy.
These steps ensure that MAC fits your organization’s data protection model.
Steps to Implement and Maintain Effective MAC Policies
Effective MAC implementation requires careful planning:
- Define clear data security levels.
- Assign access roles within your network.
- Match user clearances to data classification.
- Update the MAC system as roles or data change over time.
Additionally, remember to:
- Train staff on MAC policy.
- Monitor regularly for breaches or attempts.
- Adjust policies as new threats emerge.
In essence, MAC is a vital component for stringent data security. It’s a robust model that needs attention to detail for successful implementation and maintenance. Through regular review and adjustment, MAC can safeguard your organization’s most sensitive assets.