Fire safety is a critical aspect of both personal and public safety. Whether you’re at home, in an office, or at a factory, understanding fire extinguisher classifications can be the key to preventing devastating damage and ensuring a swift and effective response to fires. Knowing which type of fire extinguisher to use in various emergency situations could make all the difference in saving lives and property. In this article, we will explore the different fire extinguisher classifications and their proper uses to help you make the right choice when faced with a fire emergency.
What Are Fire Extinguisher Classifications?
Understanding the Basic Fire Classifications
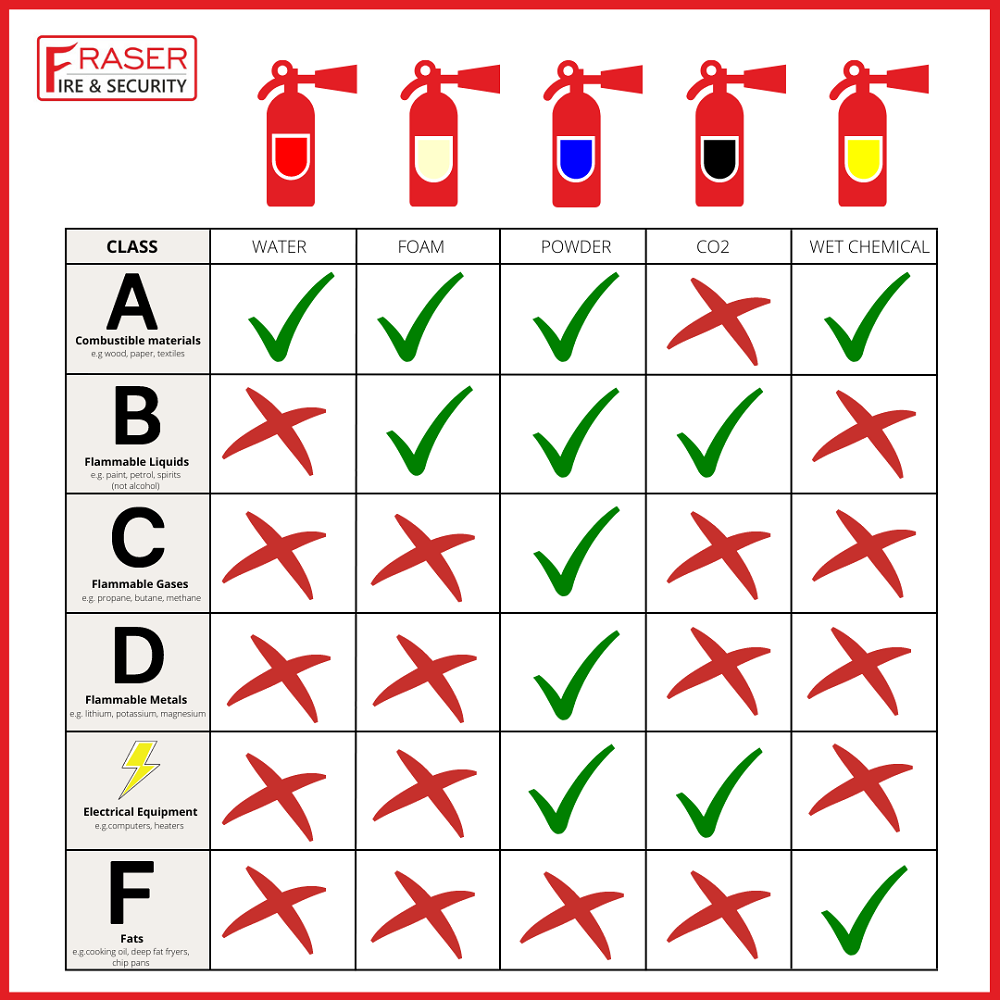
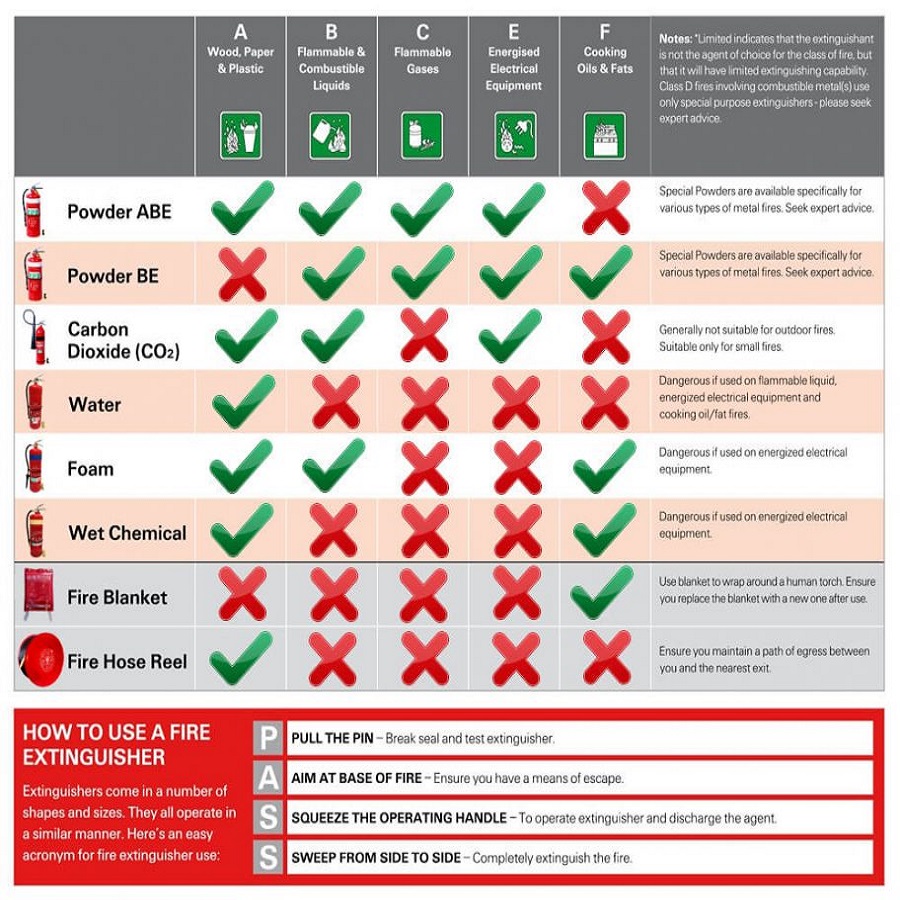
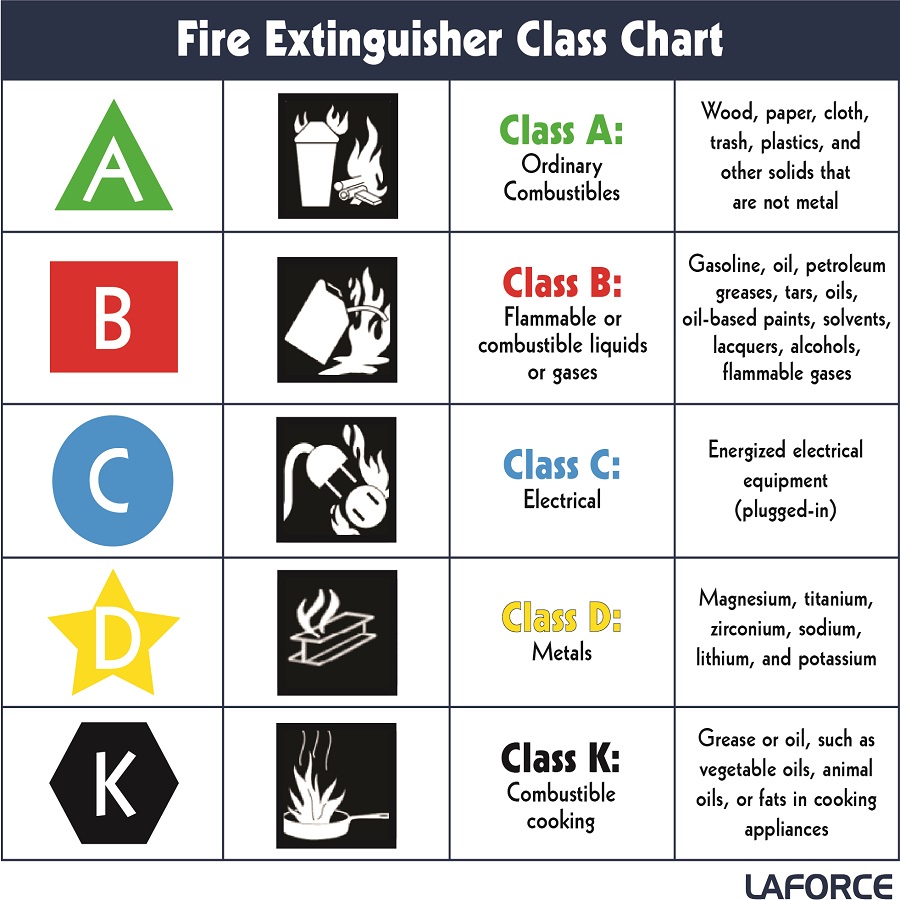
Fire extinguishers classify based on the type of fire they are designed to extinguish. The classification system create to help individuals quickly identify the appropriate extinguisher for different fire situations, reducing confusion and increasing safety. There are five main classes of fires: Class A, Class B, Class C, Class D, and Class K. Each class represents a different category of fuel or material that burns in a fire.
The fire extinguisher you use must be suited to the specific type of fire. Using the wrong type of extinguisher could worsen the situation, particularly with electrical or flammable liquid fires. It is crucial to ensure that you have the right equipment for the fire hazard present in your environment.

The Different Classes of Fires and Their Extinguishers
Class A Fires: Combustible Materials
Class A fires are the most common type of fires, involving ordinary materials that are easily flammable. These include wood, paper, plastics, rubber, and textiles. Since these materials are often found in homes and offices, fire extinguishers designed for Class A fires are vital for everyday fire safety.
For Class A fires, water-based extinguishers (such as water or foam extinguishers) are the most effective. Water-based extinguishers work by cooling down the flames and reducing the heat, which suppresses the fire. Foam fire extinguishers can also use for Class A fires as they create a barrier between the fire and the air, depriving the fire of oxygen, which helps to extinguish it.
It is important to note that water-based extinguishers should never use on electrical fires (Class C) or flammable liquid fires (Class B) as this could lead to dangerous electrical shocks or cause the fire to spread more rapidly.
Class B Fires: Flammable Liquids and Gases
Class B fires involve flammable liquids such as gasoline, oil, paint, alcohol, and solvents, as well as gases like propane and butane. These types of fires can spread quickly and are particularly dangerous because liquids can spill and spread the fire over a larger area.
For Class B fires, fire extinguishers that use foam, dry chemical powder, or CO2 (carbon dioxide) are the most effective. Foam fire extinguishers work well by smothering the fire and forming a foam blanket over the liquid, preventing further oxygen from fueling the flames. CO2 extinguishers are also highly effective because they displace the oxygen around the fire, causing it to suffocate.
Dry chemical fire extinguishers, often labeled as “ABC extinguishers,” are also suitable for Class B fires, as they work by interrupting the chemical reaction that fuels the fire. These extinguishers are versatile and can also be used for Class A and Class C fires, making them a great all-purpose option for many environments.
Class C Fires: Electrical Fires
Class C fires are electrical fires that occur when electrical equipment such as wiring, circuit breakers, and electrical appliances catch fire. These fires present a significant risk because water-based extinguishers should never be used on live electrical equipment due to the risk of electrical shock.
For Class C fires, non-conductive extinguishers are essential. The best option is a CO2 extinguisher, as it doesn’t leave any residue and does not conduct electricity, making it safe for use on electrical fires. Dry chemical extinguishers (especially those rated as ABC) are also suitable for electrical fires because they also do not conduct electricity.
When using a fire extinguisher on an electrical fire, it is important to cut the power to the electrical source if possible. This will help to prevent the fire from reigniting once extinguished.
Class D Fires: Combustible Metals
Class D fires involve combustible metals such as magnesium, sodium, potassium, and aluminum. These fires are unique and dangerous because water or standard fire extinguishers should never be used on them. Water can react violently with certain metals, causing the fire to spread even further or creating harmful explosions.
For Class D fires, special fire extinguishers designed for metal fires must be used. These extinguishers typically contain a dry powder that is effective in smothering the fire and absorbing heat. The powder works by cutting off the oxygen supply to the fire while preventing a reaction with the metal.
Metal fire extinguishers, often labeling with a specific symbol indicating their suitability for use on these types of fires. Since metal fires can escalate rapidly, it is essential to have the correct extinguisher on hand in environments where these metals are handled or stored.
Class K Fires: Cooking Oils and Fats
Class K fires are unique to kitchens and involve cooking oils or fats, typically in commercial kitchens or restaurants. These fires often cause by overheated oils or fats, such as those in deep fryers, which can ignite quickly and spread rapidly.
Class K fire extinguishers design to handle cooking oil fires and typically contain a wet chemical agent that works by cooling and chemically interacting with the oil to form a soapy layer, which prevents the fire from reigniting. These extinguishers are essential in environments where cooking oils or fats use in large quantities.
Using the wrong type of fire extinguisher, such as a water-based one, on a Class K fire can cause the fire to explode and spread rapidly, making the situation much worse. Therefore, specialized wet chemical extinguishers are the most effective for these types of fires.
How to Choose the Right Fire Extinguisher for Your Needs
Consider the Type of Hazard in Your Environment
When selecting a fire extinguisher for your home or business, it’s essential to consider the specific fire hazards present in your environment. For example, a kitchen should equipd with a Class K extinguisher, while a workshop with electrical equipment and flammable liquids may require both ABC and CO2 extinguishers. Having a variety of fire extinguishers for different situations will ensure that you prepare for any fire emergency.
You should also consider the size and accessibility of fire extinguishers. Larger extinguishers are better for bigger areas or spaces where fires are more likely to escalate, while smaller extinguishers are suitable for confined spaces or home use. Additionally, fire extinguishers should be easy to access and properly maintained.
Check Fire Extinguisher Ratings
Each fire extinguisher has a rating that indicates its effectiveness for different types of fires. The rating usually appears on the label or body of the extinguisher. The higher the rating, the more capable the extinguisher is of handling the size and intensity of a fire.
For example, an extinguisher rated “2A:10B:C” can handle a fire involving 2A (Class A materials), 10B (Class B materials), and electrical equipment (Class C). This rating helps you understand the extinguisher’s capacity to fight fires of varying degrees and categories.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection of Fire Extinguishers
Importance of Proper Maintenance
A fire extinguisher is only effective if it is in good working condition when needed. Regular maintenance and inspection are critical to ensuring that your fire extinguishers will function properly during an emergency. This includes checking the pressure gauge, inspecting for physical damage, ensuring the safety pin is intact, and making sure that the nozzle is free of obstructions.
It is important to follow local regulations for fire extinguisher inspection, which may require professional maintenance at regular intervals, typically every year. Fire extinguishers should also replace if they use or if they have expired, as older extinguishers may lose their effectiveness.
Training on Fire Extinguisher Use
Even with the right fire extinguisher, it is important to know how to use it correctly. Many organizations offer fire safety training courses, which can help people understand how to handle various types of fire extinguishers. Knowing how to use an extinguisher properly can make a life-saving difference in an emergency situation.
Conclusion: The Importance of Fire Extinguisher Classification
Understanding fire extinguisher classifications is essential for safety in any environment. Each class of fire requires a different approach to extinguishing the flames, and knowing which extinguisher to use can help prevent the fire from spreading or worsening. By selecting the correct type of fire extinguisher for the hazards in your area and performing regular maintenance, you can ensure a quick and effective response to fire emergencies.
Remember, fire extinguishers are vital tools that can save lives and minimize property damage. Properly educating yourself and others about fire extinguisher classifications and maintenance is an investment in safety that should never overlook.


